Towers of Innovation
"There is an attractive element in the colossal...[W]hat
visitor is insensitive before [the Pyramids]? And what is the
source of this admiration if not the immensity of the effort
and the grandeur of the result? The Tower will be the tallest
structure ever built by man. Will it not be grand in its own
right?" The builders of the World Trade Center had visions of grandeur similar to those of the architect of the Eiffel Tower, which, at just over 1,000 feet, became the world's tallest structure when it was completed in 1889. When the 1,350-foot World Trade Center was finished 84 years later, it, too, gained the distinction of becoming humankind's most towering tower. Both buildings, the French and the American, were to stand as potent ideological symbols—the one of the French Revolution and its impact, the other, the might of American capitalist society. The World Trade Center was born of Camelot, the John Kennedy era of irrepressible optimism. In 1961, the same year the Port Authority of New York and New Jersey recommended building a world trade center, Kennedy declared his intention to land a man on the moon by the end of the decade. In an editorial the year before, the New York Times had made its position on the World Trade Center clear: They are thinking large in downtown Manhattan. The World Trade Center ... is the most important project for the economic future of the Port of New York launched for many a year. Another Rockefeller centerThe one who was "thinking large" was David Rockefeller. The grandson of John D. Rockefeller, the founder of Standard Oil and America's first billionaire, David Rockefeller hoped to revitalize Lower Manhattan. This area, the oldest part of town, had not seen the same post-war growth as had mid-town—growth that Rockefeller Center had triggered when it rose in the 1930s. David Rockefeller's first effort in this area was the 60-story Chase Manhattan Bank Tower, completed in the financial district in 1961. (He was chairman of the bank at the time.) Even earlier, in the late 1950s, he had begun pushing hard for a world trade center. With the support of his brother Nelson, then governor of New York, he had the Port Authority evaluate plans for such a center. The Port Authority, a bistate agency responsible for ports, airports, and the like lying within 25 miles of the Statue of Liberty, determined it was feasible, and the project was underway. After years of negotiations, debate, and drawing up and redrawing up of plans, it was decided that the World Trade Center would consist of 15 million square feet of floor space distributed among seven buildings. These would include two towers that would soar over a quarter mile into the sky. The towers would top the Empire State Building by 100 feet. Some people, architects among them, wondered: Could such lofty skyscrapers be built? Building the bathtubIn the end, several technological innovations made the World Trade Center possible. These innovations solved problems that might have given pause to a man less forcibly visionary than Guy Tozzoli, head of the Port Authority's World Trade Center Department. But Tozzoli had had years of experience managing large Port Authority projects, and "can't be done" was not a phrase he brooked. The first problem didn't have to do with the towers themselves but with the ground beneath them. Much of the World Trade Center site lay atop landfill, which, over the centuries since Henry Hudson had, in 1609, first explored the river that would bear his name, had extended the west side of Lower Manhattan 700 feet out into the Hudson. Half of the 16-acre site was to be built where the river used to flow. All told, Tozzoli's crews would have to excavate over a million cubic yards of fill to be able to set the World Trade Center on bedrock. The question was how to keep the Hudson out. Jack Kyle, chief engineer at the Port Authority, came up with an answer. It was known as the slurry trench method. Excavating machines with clamshell buckets dug a three-foot-wide trench right down to bedrock 70 feet below. They did it in 22-foot-wide sections all the way around the site. As they removed fill from each section, they pumped in a slurry of water and bentonite, an expansive clay. The clay naturally plugged any holes in the sides of the dirt walls. 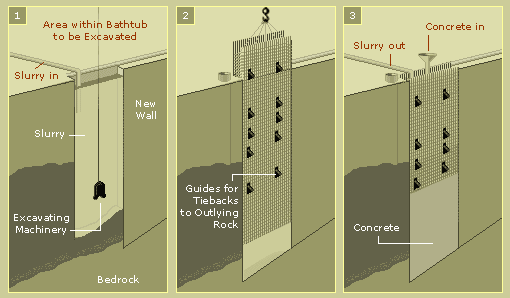
(1) Builders of the "bathtub" wall first excavated a three-foot-thick trench segment that was 65 feet deep by 22 feet wide and filled it with a stabilizing slurry. (2) They then lowered a giant steel cage into the trench, with attachment points for reinforcing tiebacks that were later anchored to bedrock outside the wall. (3) Finally, they poured in concrete, which, as it rose from the bottom up, forced out the temporary slurry. When they had fully excavated a section of the trench, workers slid a 25-ton, seven-story-high cage of reinforced steel into the section, then filled that portion of the trench with concrete from the bottom up. The yard-thick wall became known as the "bathtub," though this bathtub was meant to keep water out, not in. When the last of 152 sections became a wall, then and only then could excavators begin removing earth from within the tub. Rather than having the fill hauled away, Tozzoli donated it to the city, spreading it as new landfill southwest of the site. In this way, the City of New York received $90 million worth of newly minted real estate, on which developers later built Battery Park City. Elevators like subwaysThe second problem that Tozzoli's team addressed concerned elevators. Ironically, while the invention of elevators had made skyscrapers possible, elevators were thought to limit how high skyscrapers could go. The more floors you have, the more people you have; the more people you have, the more elevators you need; the more elevators you need, the less space you have to rent to pay for all those floors. This conundrum was one of the reasons, if not the chief one, why skyscrapers rarely reached beyond 80 floors. Undaunted, Tozzoli's group devised a solution. They would design the elevator system to mimic a subway system, with express and local elevators. In the World Trade Center, giant express elevators, each capable of carrying 55 passengers and rising at 1,600 feet per minute, zipped up to "skylobbies" on the 44th and 78th floors. Here passengers exited on the side opposite from where they had entered and crossed the lobby to pick up local lifts. Each tower also had a single express elevator that went all the way to the top. The one in the South Tower went to the observation deck, that in the North Tower to the Windows on the World restaurant. The beauty of this system lay in its economy of space. Local elevators for the lower, middle, and upper zones of the building sat one atop the other in the same shafts. And since the express elevators to the skylobbies traveled no farther than the 44th and 78th floors, respectively, the higher one ascended in the building, the less space had to be given over to elevator shafts. It was, as Angus Kress Gillespie, author of the book Twin Towers, put it, "a pioneering translation into the vertical of horizontal mass transportation." The result: 75 percent of the floor space in each tower was rentable, a significant improvement over 62 percent, the highest yield achieved in earlier skyscrapers. A tube of a towerThat 75 percent was also made possible by another innovation. Previous high-rises had relied for their structural integrity on a forest of supporting columns on each floor. Typically, architects spaced these 30 feet apart throughout the interior. The exterior walls of such buildings were merely curtain walls, which let light in and kept weather out but provided little support. Such was not the case in the World Trade Center. Consulting engineers Leslie Robertson and John Skilling invented an entirely new method of construction. The forest of interior columns vanished; such columns only appeared in and around the central core of elevator shafts, stairwells, and bathrooms. Then it was nothing but open space—60 feet of it on two sides, 35 on the other two sides—before one reached the outside walls. These were not curtain walls but cages of steel columns spaced just over a yard apart, with 22 inches of glass in between. (Minoru Yamasaki, the building's architect, designed it this way in part because he was insecure with heights and felt more comfortable with such narrow windows.) The shafts of steel in the exterior walls shouldered not only gravity loads pressing down from above but also lateral loads caused by gusty winds nudging the building from the side. Such tube-style architecture relied on high-strength steel, which was only then becoming available. It resulted in up to an acre of rentable space on each floor, and it became the pioneering style of frame for a whole new generation of buildings. Damping the swayAs sturdy as these towers would be, Robertson and Skilling knew they would still be flexible in high winds. Indeed, they designed them to be so. But they realized the swaying effect, especially in strong gusts, might bother tenants high in the building. So they fashioned yet another innovation, a state-of-the-art damping system. Like door closers or car shocks, the dampers absorbed the wind's punch, easing the towers one way or the other so smoothly that office workers hardly noticed the movement. The dampers were made of visco-elastic material. "These are materials that are partially viscous, that is, partially flowable like oil, and also elastic, which means they act somewhat like steel, in that if you strain them they return to their original shape," Robertson says. "So the material is in between those two materials—it's not like oil, it's not like steel, it's visco-elastic." Robertson's crew placed the dampers, 11,000 of them in each building, between the bottom of the floor trusses and the columns—two parts of the building that tended to move with respect to each other when the edifice swayed. When it did so, those two parts would shear the visco-elastic dampers. This shearing caused the material to heat up, and that heat was transferred to the building. "So we take the energy of the wind, and we heat the building with it," Robertson says with a note of pride in his voice. ReactionsSuch innovations meant nothing to the tower's critics, however. Both before and after the World Trade Center's official dedication in April 1973, certain vocal members of the American intelligentsia went after it as assiduously as those who let their feelings about the Eiffel Tower be known by signing a petition against its construction. (These included the writers Guy de Maupassant and Emile Zola.) The philosopher Lewis Mumford, a noted architectural critic who died in 1990, railed against the building's "purposeless gigantism and technological exhibitionism." The architect Charles Jencks went so far as to liken the use of redundancy in the towers' design to fascist methods. "Repetitive architecture can put you to sleep," he wrote. "Both Mussolini and Hitler used it as a form of thought control knowing that before people can be coerced they first have to be hypnotized and then bored." The jabs came not just from architects. New York Times columnist Russell Baker noted that the towers "seem to go on and on and on endlessly in the upward dimension, as though being constructed by battalions of exuberantly unstoppable madmen determined to keep building until the architect decides what kind of top he wants." Yamasaki, the architect, must have been stung by such comments. He saw his creation in a completely different light. In his book Architects on Architecture, the author Paul Heyer quotes Yamasaki as saying, "World trade means world peace, and consequently the World Trade Center buildings in New York ... had a bigger purpose than just to provide room for tenants. The World Trade Center is a living symbol of man's dedication to world peace." Tragically, since the heinous attacks of September 11th, 2001, the towers have become instead a symbol of international terrorism. Apart from the loss of life, Yamasaki would surely have been appalled and horrified if he had had any idea that such a fate awaited his "monument to peace," as he once called it. Had he lived to witness that awful day, he might have gone on to design differently in the future, for such Eiffelesque grandeur was not his natural inclination. As he once wrote, "As an architect, if I had no economic or social limitations, I'd solve all my problems with one-story buildings. Imagine how pleasant it would be to always work and plan spaces overlooking lovely gardens filled with flowers."
Fortunately, Yamasaki did not have to watch his beloved towers
fall. He died in 1986 at the age of 73, with his best-known
work still standing tall above Manhattan, "grand in its own
right."
Further reading Divided We Stand: A Biography of New York's World Trade Center, by Eric Darton. New York: Basic Books, 1999. |

Reaching new heights: When they were completed, the Eiffel Tower and the World Trade Center each topped all other structures then standing. 
In this photograph from the early 1960s, Minoru Yamasaki, architect of the World Trade Center, indicates in a model the site for the new complex in Lower Manhattan. 
Fill excavated from the site of the World Trade Center, seen here during construction in 1971, later provided the foundation for the World Financial Center and Battery Park City, which rose to the left of the World Trade Center in this image, on the other side of West St. 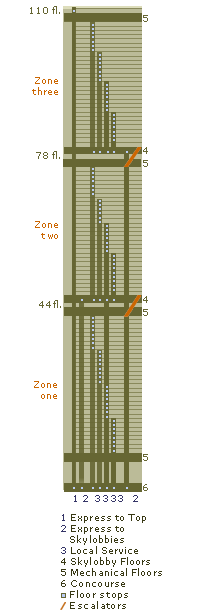
The towers' pioneering "skylobby" system, which separated express and local elevators, maximized efficiency of transport and economy of space. 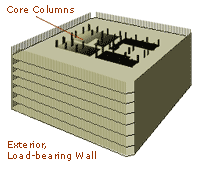
The World Trade Center's tube-style construction, with steel columns found only along the exterior wall and within a central core, freed up nearly an acre of space on each floor for offices. 
Each of the Twin Towers had 11,000 built-in shock absorbers to lessen the buildings' sway in strong wind. Surpassing Facts
Number of stories in each tower
110
Sources: |
|
|
|
|
Note: This feature originally appeared on NOVA's "Why the Towers Fell" Web site, which has been subsumed into the "Building on Ground Zero" Web site. Peter Tyson is editor in chief of NOVA online. Building on Ground Zero Home | Send Feedback | Image Credits | Support NOVA |
© | Created August 2006 |

