|
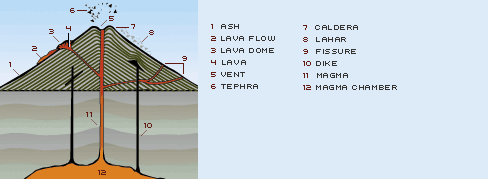
Fissure
On volcanoes, a fissure is an elongated fracture or crack at the
surface from which
lava erupts. Fissure
eruptions typically dwindle to a central
vent after a period of
hours or days. Occasionally, lava will flow back into the ground by
pouring into a crack or an open eruptive fissure, a process called
drainback; sometimes lava will flow back into the same fissure from
which it erupted.
Left: A close-up of a crack in the volcanic surface of a
cooled lava flow from the crater of Mt. St. Helens.
|