
|
 |
 |
by Gary Crawford The ringing telephone broke the evening silence. It was the fall of 1983, and my research partner, Professor Masakazu Yoshizaki, was calling from Japan. "Gary, I have some news," Yoshi said. "We have a few grains of barley from a site on the Hokkaido University campus. I think you should come and look at them." The Japanese language is notorious for its ambiguity, so I wasn't quite sure of the full meaning of what I had just heard. But I didn't need to know much more. Though it may sound like a trivial piece of news to you, I knew something was up, and it deserved closer scrutiny. My teaching schedule at the University of Toronto kept me from hopping on a plane for several months, but when I finally got to the lab on Hokkaido, the northernmost island of Japan, I realized the full import of Yoshi's news - namely, that the history of Hokkaido's indigenous people, the Ainu, was about to be rewritten. Since the mid-1970s I had been investigating the relationship between plants and people in prehistoric northeastern Japan, particularly Hokkaido, using an archeological tool called flotation. The widespread use of this technique beginning in the 1960s sparked a quiet revolution in archeology. Flotation facilitates the collection of plant remains, mainly seeds and charcoal, preserved by burning in oxygen-poor environments such as the depths of a fireplace. Under these circumstances, seeds don't oxidize to ashy dust. One can recover the resulting carbonized seeds by sampling soil from ancient hearths, floors, pits, garbage dumps, and the like. One places the soil gently in water, stirs it so the carbonized material floats to the surface, and then decants the water and its floating contents through a fine mesh, which traps the floating plant material while allowing the water to pass through.
The archeological grain from Sakushukotoni-gawa ("gawa" means river), as the campus site is known, dated to A.D. 700 to 900. The site is contemporaneous with the medieval Japanese to the south, who had been forging a nation-state for several centuries. The immediate predecessors of the Ainu, who are the native people of northeastern Japan, occupied the site. Many archeologists consider the Ainu to be the last living descendants of the Jomon people, who lived throughout Japan from as early as 13,000 years ago. The Jomon are known for their elaborate earthenware, which they often decorated with cord (rope) impressions, and for their stone tools, pit-house villages, and, by 1500 B.C., elaborate cemeteries marked by stone circles or high earth embankments. To a large degree, the Jomon relied on hunting, fishing, and collecting plants and shellfish for their subsistence.
To a large extent, this also seemed to be the case in northeastern Japan. Archeologists and historians have long described the Ainu, like the Jomon, as hunter-fisher-collectors and, because the two peoples lived in the same region, they had few qualms about assuming the Ainu were living representatives of Jomon culture. However, the Ainu, at least in the last few centuries according to historic records, lived in above-ground, rectangular dwellings and used metal tools as well as wooden and ceramic bowls, pots, and dishes. These characteristics contrast with those of the Jomon, but in the minds of historians and archeologists it was the lack of agriculture in both cultures that forged the link between the Ainu and Jomon cultures. Further bolstering this opinion, the skeletal biology of Jomon populations demonstrates a strong resemblance and therefore a close affinity to the Ainu. Justifiably, the Ainu seemed a relic of a primitive hunting-and-gathering people who had inhabited northeastern Japan for thousands of years. Continue: The Relationship between the Jomon and the Ainu Origins of the Ainu | Ainu Legends | Find Your Way Resources | Transcript | Site Map Editor's Picks | Previous Sites | Join Us/E-mail | TV/Web Schedule About NOVA | Teachers | Site Map | Shop | Jobs | Search | To print PBS Online | NOVA Online | WGBH © | Updated November 2000 |
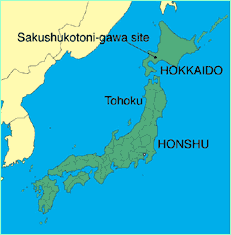 A map of Japan showing the fateful site of
Sakushukotoni-gawa on Hokkaido.
A map of Japan showing the fateful site of
Sakushukotoni-gawa on Hokkaido.
 A flotation screen with a recovered sample.
A flotation screen with a recovered sample.
 An early Jomon pit house.
An early Jomon pit house.