|

|
|
|
|
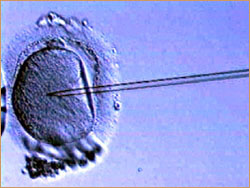 In ICSI, a single sperm is injected into the
mother's egg.
In ICSI, a single sperm is injected into the
mother's egg.
|
Glossary
Back to The 18 Ways
Artificial insemination:
Introducing semen into the uterus or oviduct by other than
natural means.
Cloning: Taking
body (i.e., non-sex) cells from an adult and introducing
them into an unfertilized egg that has had its genetic
material removed, and then encouraging embryo
development.
Cytoplasm: The
complex of organic and inorganic substances within a cell
outside of the nucleus.
Cytoplasmic transfer:
A technique in which cytoplasm from a donor egg is drawn
into a pipette containing a single sperm from the male
partner, after which that donated cytoplasm and the sperm
are injected into the patient's egg.
Frozen embryos:
Specialists may freeze additional embryos from a woman's
cycle for later use. They may also freeze embryos of a donor
in order to have them ready to place in a surrogate mother's
uterus at the appropriate moment in the surrogate's natural
or hormone-replaced cycle.
Intra-Cytoplasmic Sperm Injection, or ICSI
("ick-see"):
A technique developed in 1992 to combat male infertility in
which doctors collect a single live sperm and inject it
directly into the cytoplasm of the mother's egg.
In vitro fertilization:
Taking eggs from a woman, fertilizing them in the laboratory
with a man's sperm, and returning the resulting embryos to
her uterus several days later.
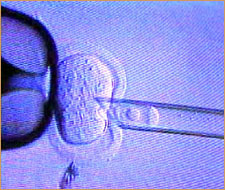 Nuclear transfer
Nuclear transfer
|
|
Nuclear transfer:
In his still-experimental technique, Dr. Jamie Grifo of New
York University Medical Center takes the nucleus of an
immature egg (i.e., one that hasn't gone through cell
division) from the mother-to-be and places it in the
enucleated (nucleus-free) egg donated by a young woman.
Grifo's hope is that the technique, when perfected, will
help older women whose eggs are less than ideal have babies
using a younger person's eggs.
Preimplantation Genetic Diagnosis, or PGD:
A technique for screening embryos prior to implantation for
genetic abnormalities. Only embryos free of such
abormalities are implanted.
Surrogate: A
surrogate mother is one who, usually by artificial
insemination or by introduction of a fertilized egg (hers or
that of a donor or the mother who will raise the child) into
her uterus, becomes pregnant and carries a baby to term for
another woman.
Back to The 18 Ways
The 18 Ways (And Then Some)
|
On Human Cloning
|
Fertility Throughout Life
|
How Cells Divide
Resources
|
Teacher's Guide
|
Transcript
|
Site Map
|
18 Ways to Make a Baby Home
Search |
Site Map
|
Previously Featured
|
Schedule
|
Feedback |
Teachers |
Shop
Join Us/E-Mail
| About NOVA |
Editor's Picks
|
Watch NOVAs Online
|
To Print
PBS Online |
NOVA Online |
WGBH
©
| Updated April 2003
|
|
|
|